AMPULES: CAUSES, CLINICAL AND TREATMENT.
An ampule is a mechanism of protection of the skin and it shows a palpable and limited cutaneous increase which has serum and lymphatic fluid. The separation or skin increase is always at an epidermic level.
The difference between ampules or phlyctenae is the diameter of the injury. In the ampules the diameter is 0,5 centimeters higher and in the phlyctenae the diameter is less than 0,5 centimeters.
There are several causes:
- By friction: it is the most frequent and it is caused by wearing shoes uncorrectly or simply because these are new and also due to long walks. The extreme temperatures (heat and cold) and humidity, make possible the appearance of ampules.
- By big sunburns.
- By chemical sunburns, mainly by acid products.
- By contact dermatitis and eczema.
- By allergic reactions.
- By some viral infections, like for example, herpes or varicella.
- By freezing.
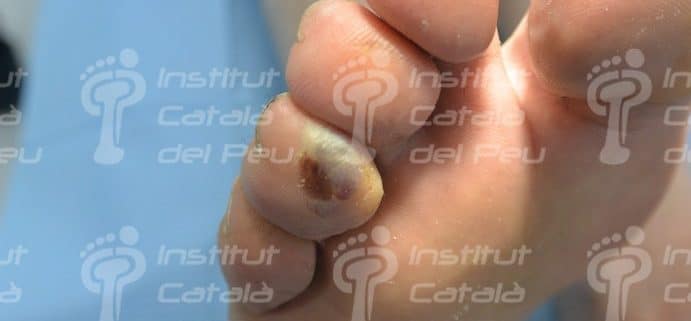
The symptoms of ampules show reddening and pain of the cutaneous surface where there are originating, lifting of the external layer of the skin and its softening due to the liquid contained inside.
The red ampules indicate that friction has caused a fracture of some blood vessel next to the cutaneous surface mixing blood with lymph. The yellowish or greenish color indicates us the possibility of an infection and, therefore, of pus inside the ampule.
It should be advisable to go to the podiatrist provided that there are ampules where come up infection signs or the affected will be a patient with risk diseases.
The treatment of ampules usually need a series of attention although small phlytenae cure by itselves.
Whenever it is treated a foot, the first thing we have to do is to wash our hands with water and soap, as well as to disinfect the ampule with some iodine. We will puncture the ampule with a sterile needle or a small bistoury in order to drain the liquid contained without cutting the skin, because the skin will work as a physiological dressing. Once the ampule is drained, we will disinfect the skin again and will apply and antibiotic cream in case it will be necessary. Depending of the size and location of the ampule, we can cover the lesion with a gauze or leave it uncovered in order to heal it more quickly.
To sum up, the use of comfortable, full, flexible shoes and seamless in the prominent zones of foot, will help to reduce the risk of these unpleasant lesions.
It is also important to wear perspiring, thin socks and of a suitable size in order to avoid wrinkles. The use of cotton socks is not recommended because they absorb the sweat and cause friction against the skin. For those sportsmen who practice running, it is advisable to apply anti-rubbing creams.
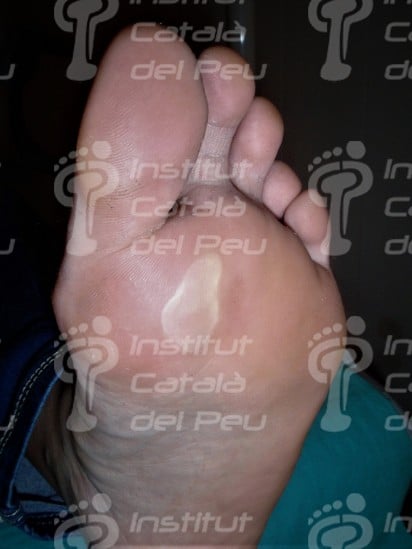
Metatarsal ampule.
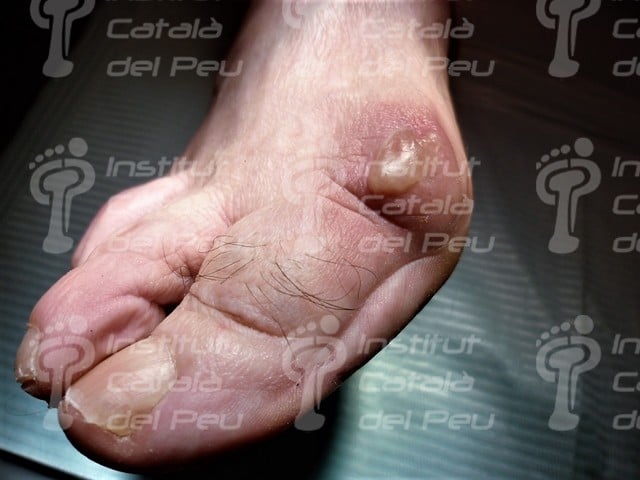
Ampule in dorsum of the bunion (by using shoes).
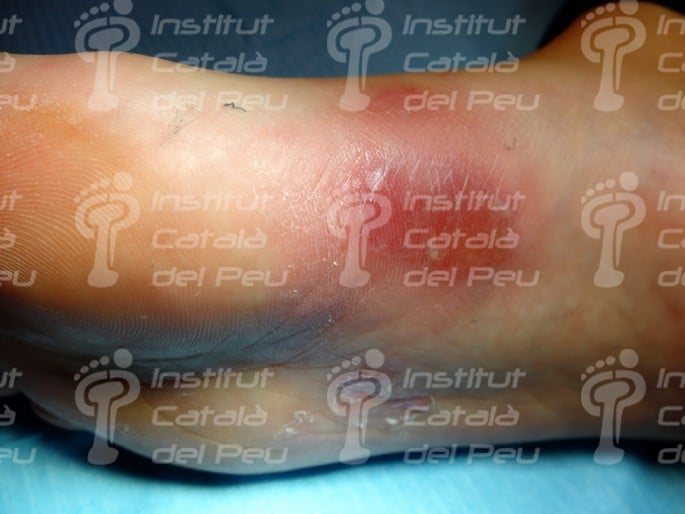
Frequent ampule in runners.
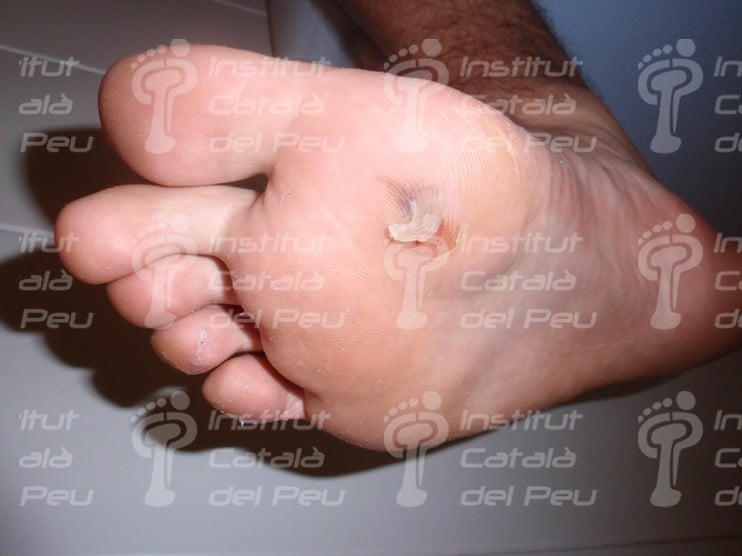
Ampule in the head of first metatarsal. The anatomy of the foot may cause the appearance of more ampules.
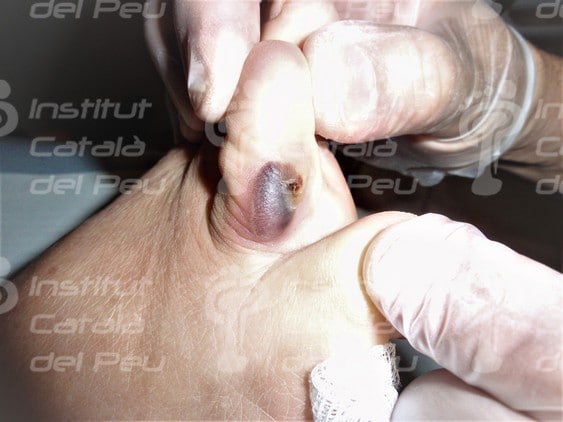
Serohematic interdigital ampule.
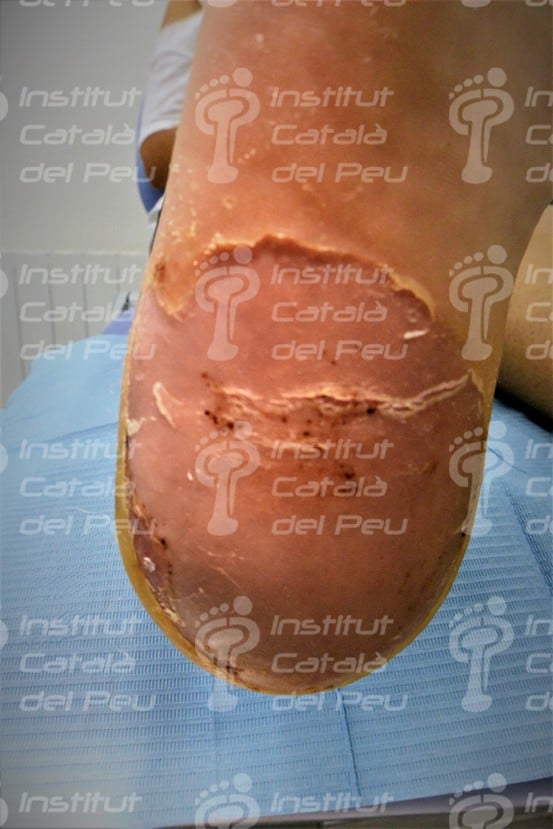
Talar ampule of five days of development.
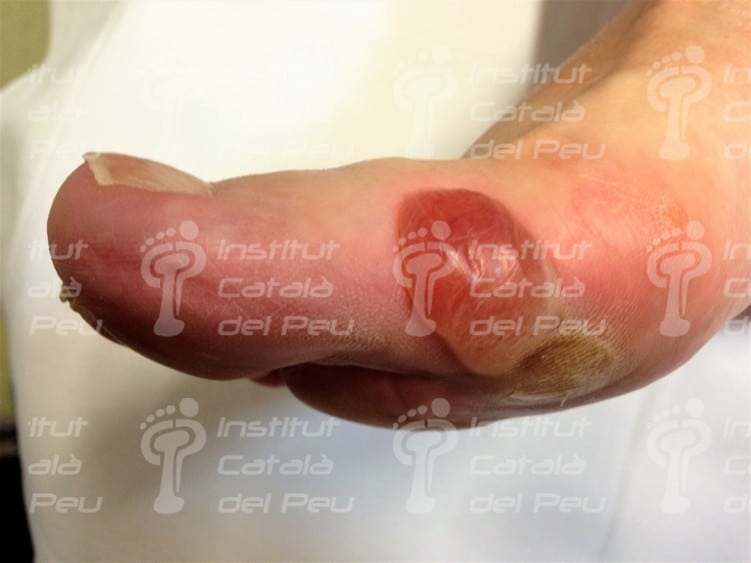
Medial ampule in hallux valgus.
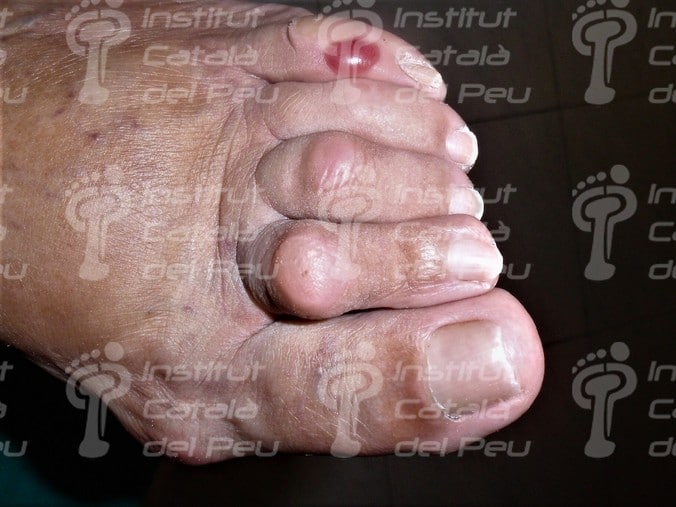
Serohematic ampule in the dorsum of the fifth toe.
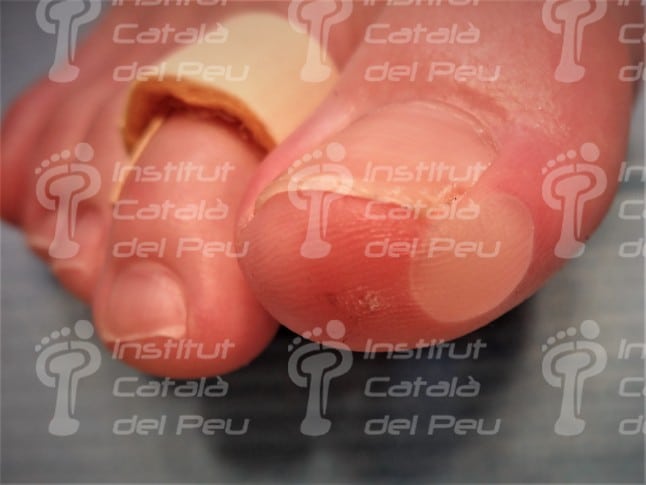

Phlyctena in the medial side of the first toe.







Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!