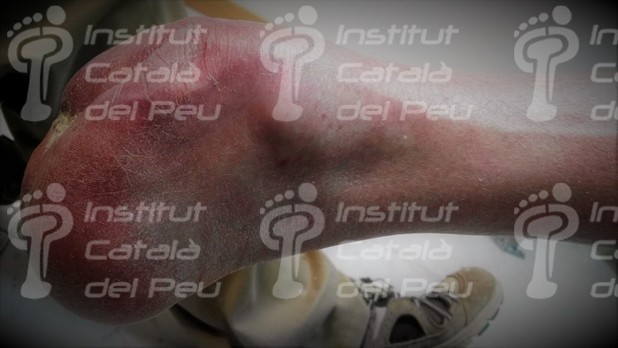
Regarding amputations, the stump’s more suitable length is the one who best keeps comfort, function and aesthetics.
The prosthesis must make an exact alignment and to have an easy and comfortable placing.
It is very important to have a static and dynamic rest, to re-establish the balance, to damp impacts, as well as to supply all the functions of the lacking joints.
The prosthesis for Chopard’s or midtarsal amputation is designed to give all the functions of the foot’s partial amputation, as well as the same lower extremity. This partial amputation of foot respects the bones of the back side of foot which are the calcaneal and the astragalus.
The prosthesis for Chopard’s amputation increases the patient’s mobility and activity providing him a much better quality of the latter by obtaining a bigger autonomy.
The aim of the prosthesis is to spread the pressure in which the stump is undergone through all the charge side as maximum as possible.
This kind of prosthesis has to make up very accurately in order to avoid excessive pressures on the osseous prominences.
The prosthesis for Chopard’s amputation holds the front part prosthetic stuffing in a front part of the foot shape with an elastic and flexible material which helps the patient to harmonize the wandering about.
The prosthesis for Chopard’s amputation is difficult to make up because this kind of amputations causes a secondary varus echino position, as a consequence of muscular disturbance. It is worth to mention that breakthroughs in the field of surgical techniques have played down this complication.
These are the different kinds of prosthesis:
- Anti-echino splint. This kind of prosthesis takes in the proximal third of the extremity and it is fitted to a prosthesis of the foot.
- Prosthesis with laminated fitting together by resin and subsequent closure with molding leather. This is a very strong kind of prosthesis and it is reinforced with a bigger adjustment allowing an important daily activity to the patient.
- Splint Rancho type with a previous amputated zone stuffing.
Coming up, we show you the making up stages of a prosthesis through an example of a destabilizing Chopard’s amputation.
Appearance of foam adapted to the stump. This is a shock-absorbing piece and protects the stump from splint stiffness.
Dorsal image of carbon fiber splint.
Prosthesis in a provisional stage. Protective splint and foam of stump.
Prosthesis in a provisional stage. Adhesion of protective foam to splint.
External lateral image of provisional prosthesis.
Front side image of provisional prosthesis.
You can watch the subjection of the prosthesis to the plantar insole through mastic.
Carbon fiber prosthesis finished.
Detail of the front part of foot.
Carbon fiber prosthesis finished. Subsequent image.
Definitive check to patient.
Definitive check to patient.