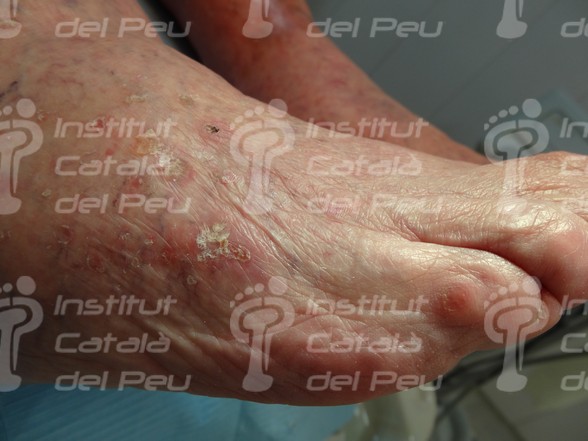
The actinic Keratosis, better known as sunspots, is a degenerative and spreading lesion of the epidermis’s cells which show small elevations and roughness of the skin. The lesions are reddish or brown color, scabby and similar to warts with an inflammation around the lesion. Sometimes, they subside and appear again with some kind of pain or burning. The actinic Keratosis may be a precursor of skin cancer, like for example, the scaly cells carcinoma.
The actinic Keratosis is caused by the constant exposure to the sunlight, although there are other factors which help its appearance. These factors are the genetic sensitivity, fair skin, fair-haired or Caucasian people, green or blue-eyed people, immune depressant medicines, the transplant of some organ, sunburns on early ages, as well as people of more than fifty years old. It is a pathology in which men are more affected than women. It appears in the face, alopecic zones of scalp, shoulders, hands, etc.
The appearance of the actinic Keratosis has increased in the last ten years regarding to other dermatosis, and in the future, it is expected an increase.
The 10 % of actinic Keratosis become malignant into scaly or spinocellullar cells carcinoma and approximately 50 % of scally cells carcinomas with a no treated actinic Keratosis. The bigger is the actinic Keratosis, the greater is the possibility that one or more than one become a skin cancer.
Nowadays, the actinic Keratosis, for some experts, it is classified like an authentic cutaneous scaly carcinoma in situ when sharing morphological features and cytogenetical changes. They don’t consider it as a precursor of the sclaly cells of the carcinoma but an initial stage of it. It is a clinical diagnosis, although in doubtful cases, it is advisable a cutaneous biopsy. The desquamation and palpation of hyperkeratosis is helpful for the diagnosis, as well as the appearance of wrinkles, atrophic skin or pigmentary alterations.
The actinic Keratosis must be treated as early as possible in order to prevent its development.
Such treatments are classified in isolated lesions treatments and treatments in the field of the effect of cancer. They are used combined in chronic actinic Keratosis and they are not exclusive to each other, although its therapeutic choice will depend on the features of the patient, amount and location of the lesions, as well as of the previous treatments received. The most common are:
- Creams for external use only, while the lesion will not degenerate, like for example, the 5-Fluorouracil at 0’5 % plus salicylic acid at 10 % or imiquimod.
- Electrosurgery with local anesthesia.
- Phototherapy, recommended in many non hyperkeratosical lesions. It consists of the application of an occluded topica photosensitizer during two or three hours and the subsequent illumination of the zone with a suitable light.
- Chemical peeling.
- Cryotherapy: application of liquid nitrogen in the lesion in order to cause necrosis and elimination of the lesion. It is recommended in isolated lesions.
- Curettage: removal of actinic Keratosis with a scalpel.
Some advices to those patients with precedents of actinic Keratosis are the following:
- Checkup of cutaneous spots. The appearance of signs like color change, shape or size of a spot could reflect the appearance of skin cancer. In these cases it is recommended to visit the dermatologist.
- Reduce the exposure to sunlight, mainly between 11.00 A.M. and 4.00 P.M. and use sunglasses, hats and suitable clothes. If it is a cloudy day, we must not underestimate the appearance of ultraviolet rays.
- Apply solar protection thirty minutes before the solar exposure and the more fair-skinned you are, use the higher protection factor. The sun exposure is more intense at the beginning of summer and the risk of burns is bigger in higher altitudes.