THE SUBUNGUINAL HEMATOMA: CAUSES AND TREATMENT
We call subunguinal hematoma the accumulation of blood under a nail, whether on the foot or the hand.Its main features are inflammation, pain, discolouration of the nail to a reddish or purple hue and tenderness.
There are numerous causes. These are mainly traumatic (shoes, impacts, etc.) and, a lesser degree, treatments with anticoagulants, chemotherapy or autoimmune diseases.
It is characterised by broken capillary vessels of the nail bed causing a hemorrhage which remains deposited between the nail bed and the nail. This extravasation of the blood creates some pressure on the adjacent tissue and thus, pain. Sometimes the pressure exerted by the hematoma breaks through the epidermis and causes a spontaneous drainage.
In severe trauma it is important to x-ray the toe to assess the presence or abscence of a fracture of the phalanx.
When faced with a subunguinal hematoma several treatments can be applied:
- Perforation of the nail with small holes to drain the accumulated blood under the nail plate. It must be done in the early stages with the aim of preventing further detachment of the nail plate.
- Partial or total exeresis of the nail provided there is an evulsion of the nail bed due to traumatism. We remove part of the nail once its anomalous movement is assessed and the possible disorders we believe its conservation may cause a posteriori.
The nail is affected by traumatism it can cause indefinite deformities of the new nail.
The absence of the nail plate over a period of time can help the development of fungal infections.
In the days after the appearance of the subunguial hematoma, anatomical shoes must be worn that so as not traumatise the nail more. It is also important to cut the nail in order to prevent accidental avulsion of the nail.
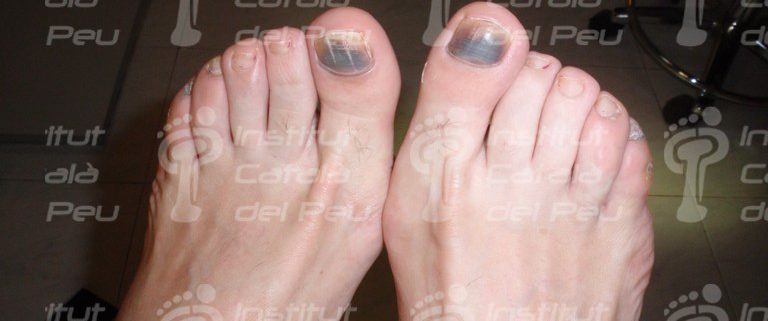
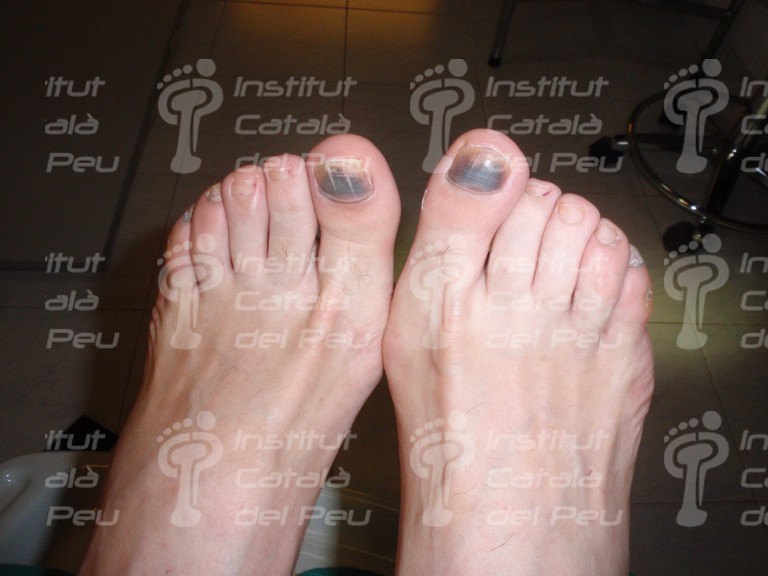 Bilateral subunguinal hematoma
Bilateral subunguinal hematoma
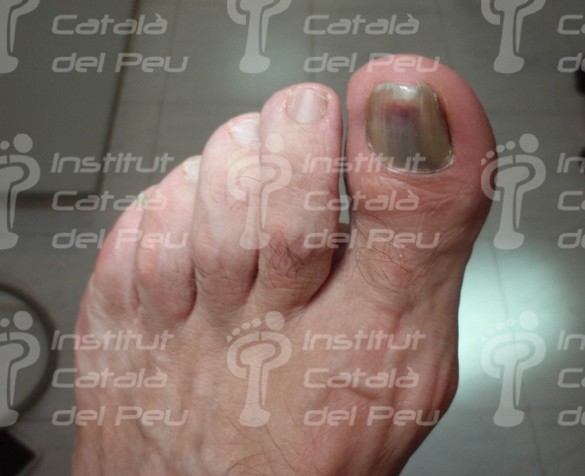 Blue-violet colour typical of a recent traumatism
Blue-violet colour typical of a recent traumatism
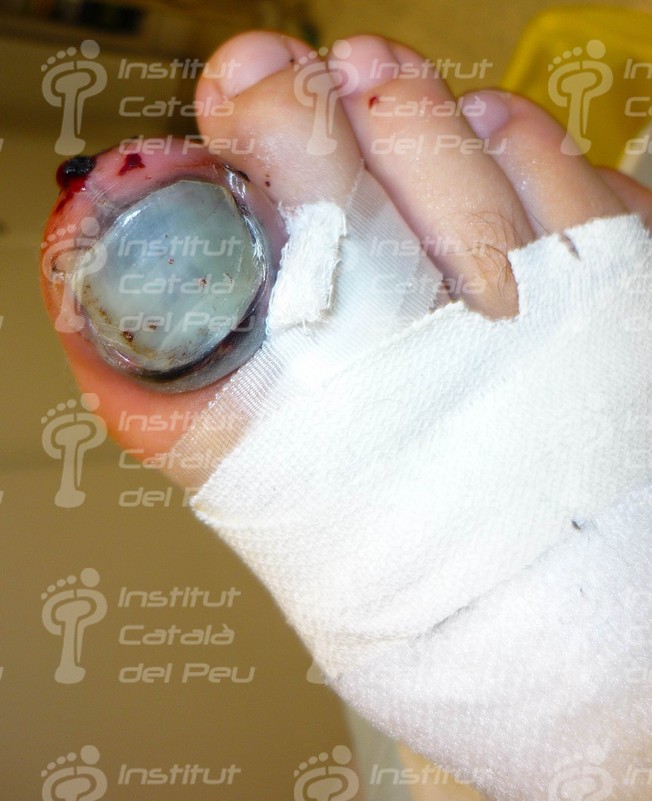
 Subunguinal hematoma at an acute stage
Subunguinal hematoma at an acute stage
 Immobilisation. It ma sometimes be accompanied by the fracture of the phalanx.
Immobilisation. It ma sometimes be accompanied by the fracture of the phalanx.
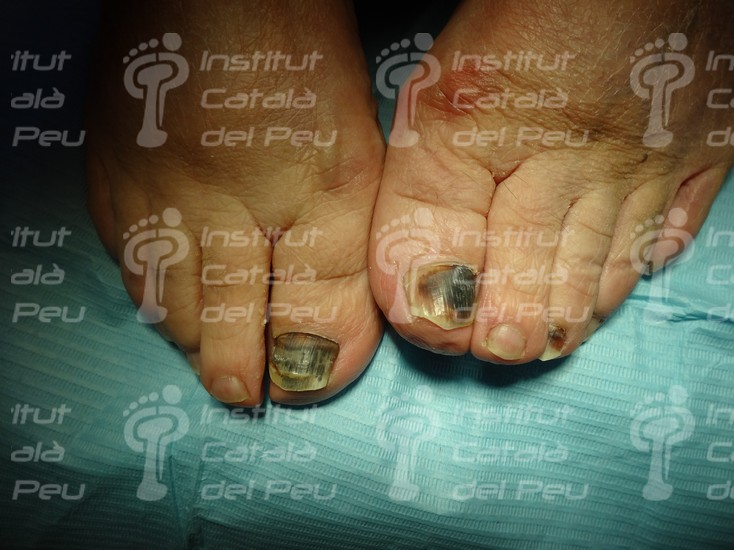 Symmetrical subunguinal hematoma (typical of shoes).
Symmetrical subunguinal hematoma (typical of shoes).
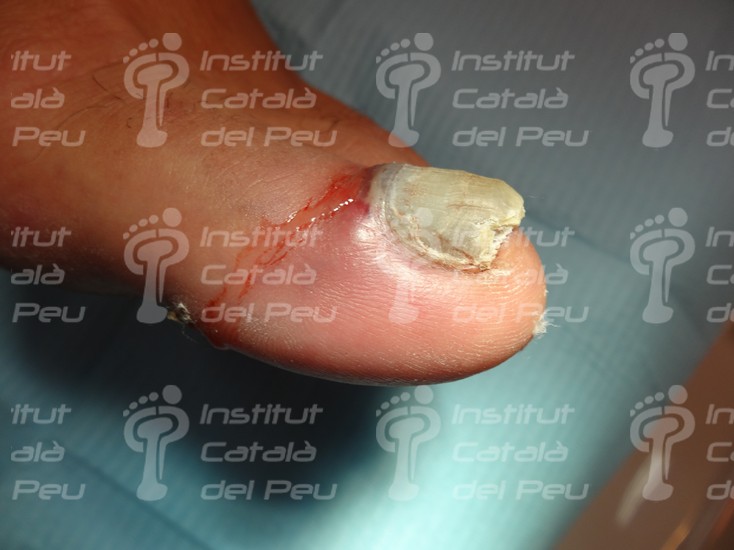
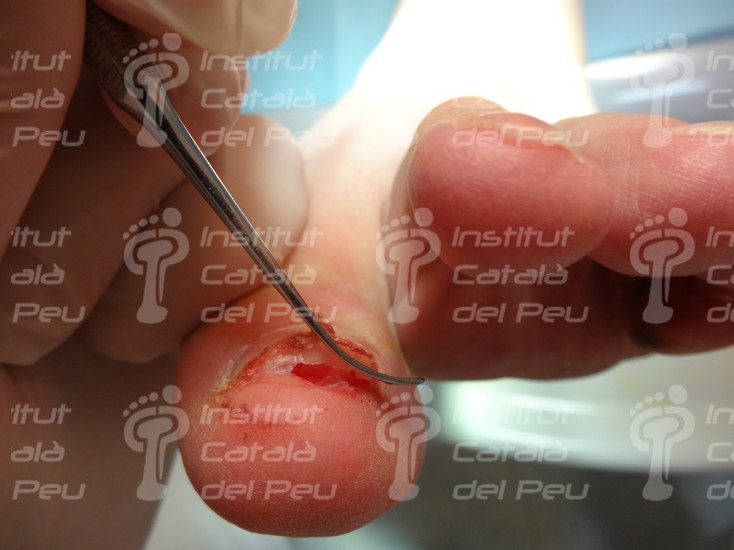 Front drainage of a subunguinal hematoma
Front drainage of a subunguinal hematoma
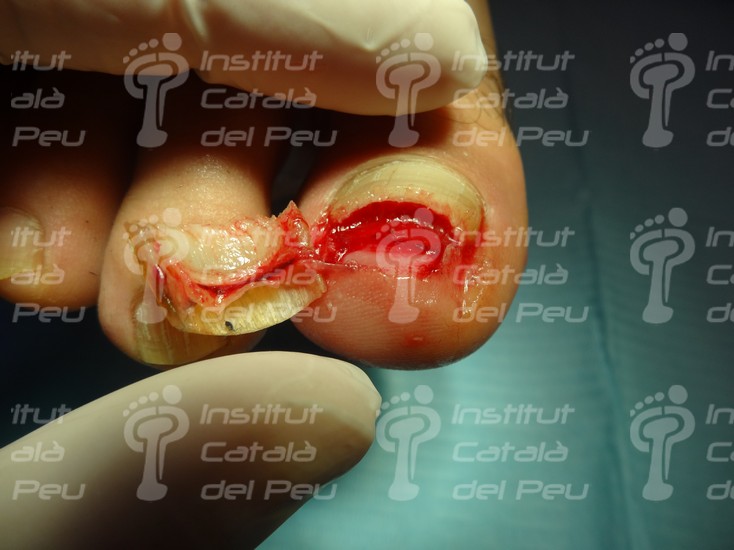 Cut and cure of an avulsion of the nail plate.
Cut and cure of an avulsion of the nail plate.
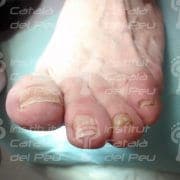
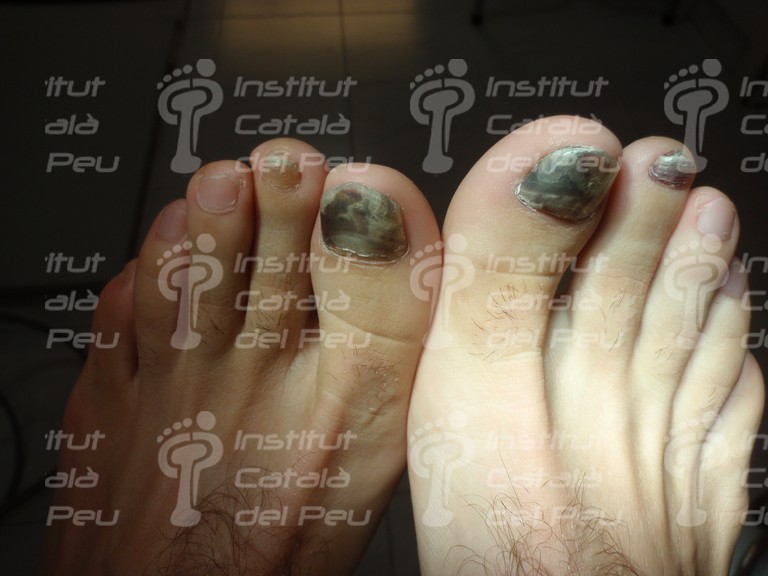 Blackish color due to coagulation (late stage).
Blackish color due to coagulation (late stage).
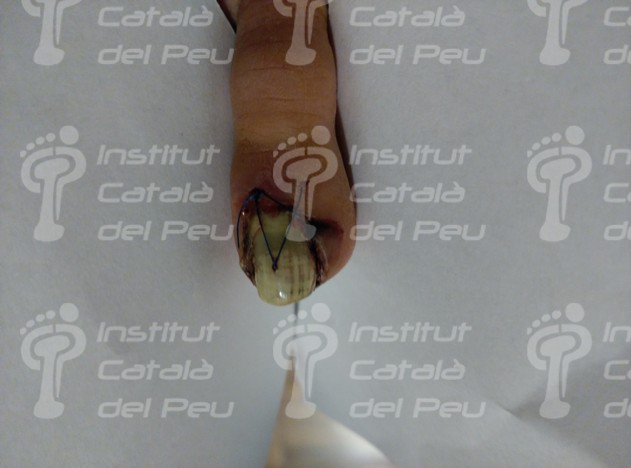 Not a recommended technique.Attachment of the nail plate via suture.
Not a recommended technique.Attachment of the nail plate via suture.







Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!