PLANTAR FASCITIS: SYMPTOMS AND TREATMENT.
The plantar fasciitis is an inflammation of a membrane or stripe of connective tissue called fascia. It is located in the sole of the foot and it takes in from the calcaneal to the proximal phalanges.
The fascia is made up of producing cells of structural elements of the conjunctive tissue, a fundamental liquid substance which shapes the structures and fibers of conjunctive tissue such as the collagen, reticular or elastic fibers.
The functions of the fascia are:
- To shape the tissues by support, suspension and stability.
- Strength transmitter. In a muscular level each fiber generates movement exerting tension on such muscular fibers.
- Helps the movement by its ability of deformation and stretching.
- Allows to restore fibrous tissues.
- It is important in the link of different osseous and muscular structures.
The most peculiar symptom of this lesion is the appearance of burning or an intense pain in the fascia insertion (internal zone of the heel), mainly when waking up in the morning, after a long time sat or when running upstairs. When starting to walk, the pain sign usually falls.
In sportsmen the pain appears after exercise and in case of not taking care of the fascia in an incipient stage, can restrict practicing sport. As a matter of fact, if pain remains, its intensity increases more and more and covers all the zone of the plantar arch taking a long time to make such pain disappear.
The causes which help the appearance of a plantar fasciitis are:
- The morphology of the foot (splay foot, claw foot, valgus foot, etc.).
- A pathological wandering about or wrong footstep.
- The reduction of the back musculature of the leg.
- Inappropriate shoes (high heels, non stabilizing shoes of the back side of the foot, etc.).
- Overweight
- Sudden changes of daily activities.
It is important to know the difference between the calcaneal spur and the plantar fasciitis. The calcaneal spur is a calcification of the insertion in the heel while fasciitis is caused by an inflammation without being accompanied by a calcaneal spur.
The other way around, calcaneal spurs are also located in a fortuitous way in radiological images and the patient not always has had previously any kind of pain.
The diagnosis is based on a physical test, the survey of the footstep and a radiological assessment, if necessary.
The treatment of plantar fasciitis on early stages consists of anti-inflammatory drugs and analgesics as well as to practice stretching exercises of the Achilles tendon, gemellus and the fascia.
The stretching of the fascia has an impact on the joints as well as in different kinds of movement.
The adhesions of the layers which form the fascia, will cause pain and a decrease of mobility. All these are typical because of traumatisms, lesions or postsurgical iatrogenia either by excess weight and hyperactivity.
To get the greatest stretching as possible, it would be ideal to stretch in different directions because fascia lays different directions across. It must be considered that fascia has a lot of collagen and water and it causes a more solid or more liquid viscoelastic capacity at certain points.
This will change depending of the temperature. For example, when we wake up in the morning, the fascia works as a solid because our temperature is lower. After warming-up exercises or wandering around for a while, the body temperature increases, therefore the fascia transforms into a liquid, being more elastic.
The basic stretching is as follow:
- Stretching with a towel:
We remain seated on the floor, stand up straight with our trunk, our legs stretched and our feet straight. We put the towel at the level of the plantar cushion (metatarsus) and the patient tractions on both sides of the towel towards himself. The traction must be kept between 15 and 30 seconds and we practice this exercise ten times.
- Use of a bottle or can as a drag roller:
Go round the bottle or the can over the bare foot ahead and backwards. Use a bottle or can just taken out from the freezer in order to apply cold simultaneously.
- Charge on a leg:
We lean on one foot and on the foot affected by fasciitis and when getting a stability point, we stand on tiptoe.
Once we stand on tiptoe, we drop the heel slowly until touching the floor. This should be practiced approximately ten times.
- Calf stretching:
Leaning on hands on a bar or a wall, we put the leg which is being treated, in a stretched way, so the plantar surface of the foot touches the floor completely (it must not lose contact with the floor when making exercise).
The other leg must be slightly bended and afterwards, we move our body ahead in order to get a traction of the calf. Keep during ten seconds the maximum tightness of the heel and repeat this exercise ten times.
- Stretching on a step or a sloping board:
Leaning on a foot on a sloping board, we bend the knee of the opposite extremity which we want to stretch. We pressure the heel down with the extremity to be stretched for one minute and we practice this exercise again five times.
In case of not improving or recidivating frequently, it should be advisable a survey of walking by the podiatrist in order to consider the use of personalized insoles which will drop the pressure in the affected zone and thus will deaden the impacts.
The advice of a type of sneaker which will not be accompanied with a survey of the footstep by the podiatrist, it has not a success guarantee.
On more advanced stages in which pain remains with frequency and intensity, we can resort to infiltrations or surgery as a last chance in case there is a chronic or a serious plantar fasciitis.
In a nutshell, it is a good prevention of the plantar fasciitis, to warm-up exercises and a specific stretching for the sole of the foot, as well as a survey of the footsteps.

A pronated foot may cause plantar fasciitis.
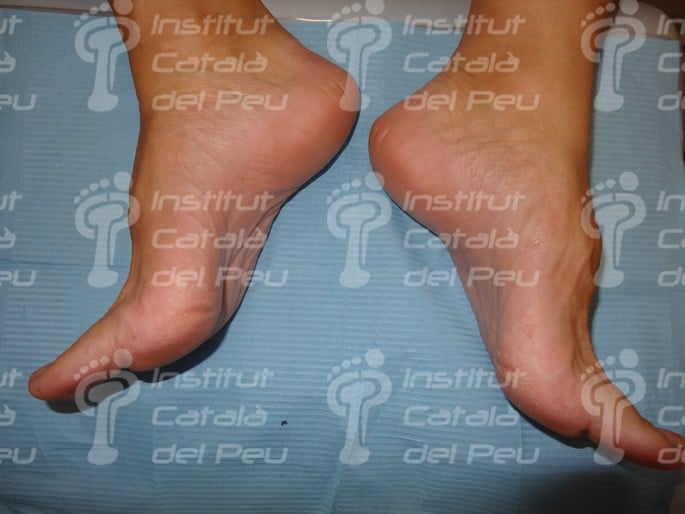
A claw foot may cause plantar fasciitis.
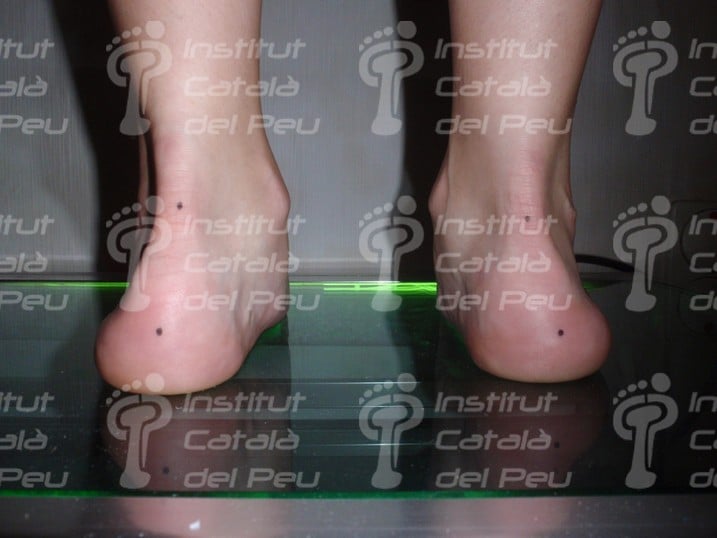
A valgus foot may cause plantar fasciitis.
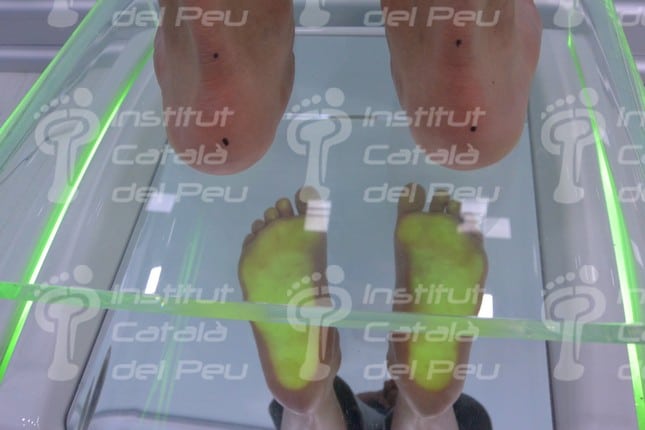
An essential flat foot may cause plantar fasciitis.
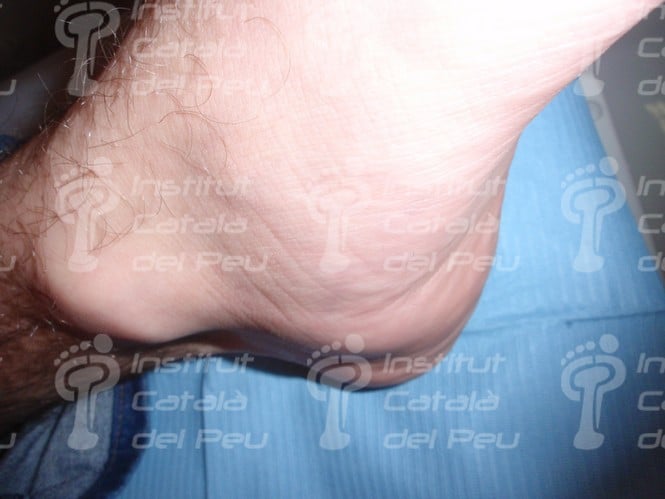
Watch the inflammation in the internal border of the heel.
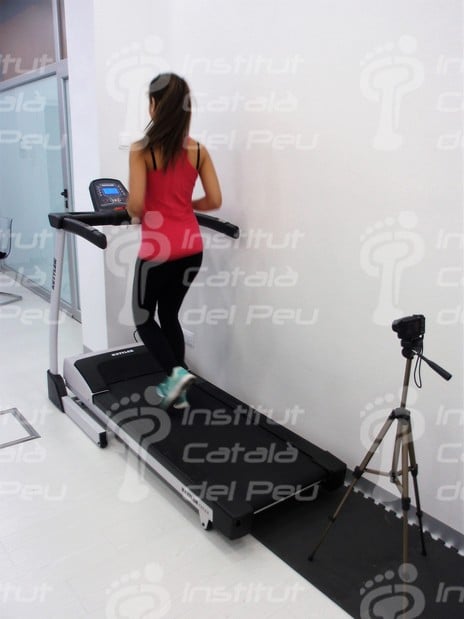

It is very important the survey of the footsteps, both in prevention and treatment.
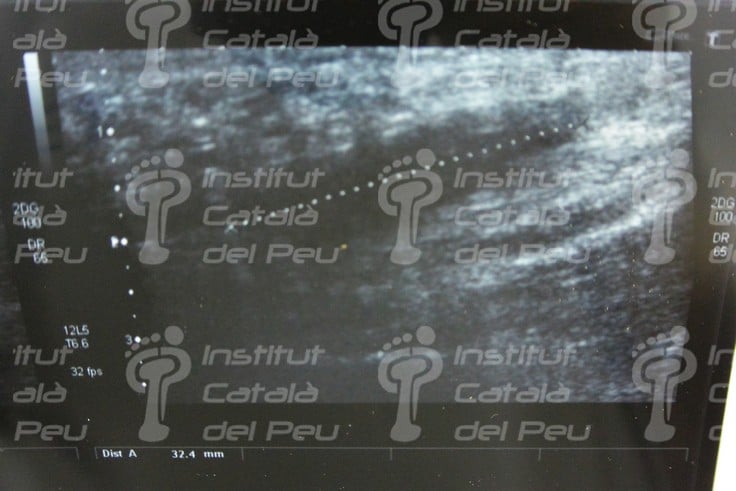
Ultrasound scan. Severe plantar fasciitis with an intra-substance fracture.
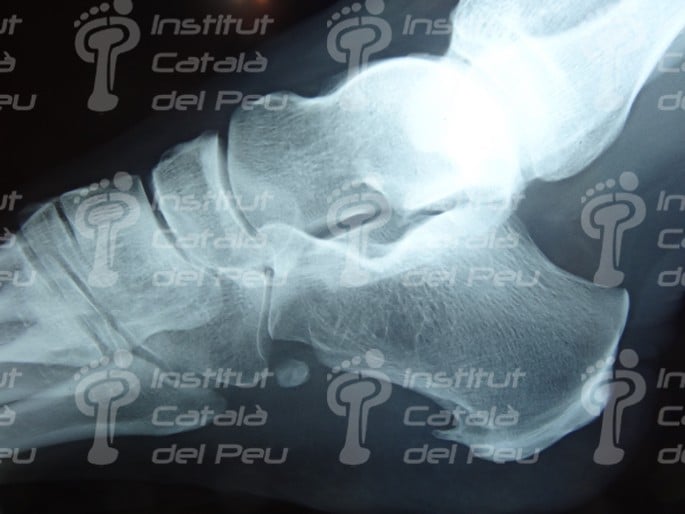
X-ray. Watch the appearance of a calcaneal spur.
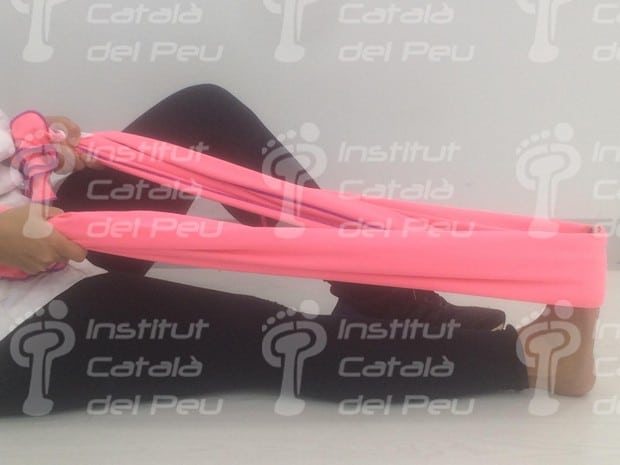

Stretching with a towel.
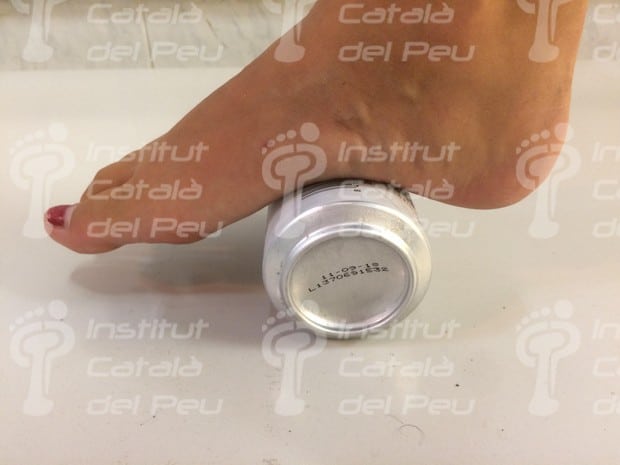

Rolling with a can.
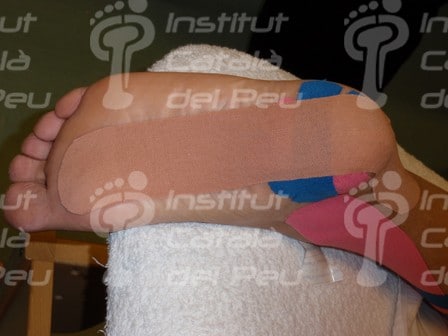
Application of a neuromuscular bandage because of plantar fasciitis and calcaneal spur.
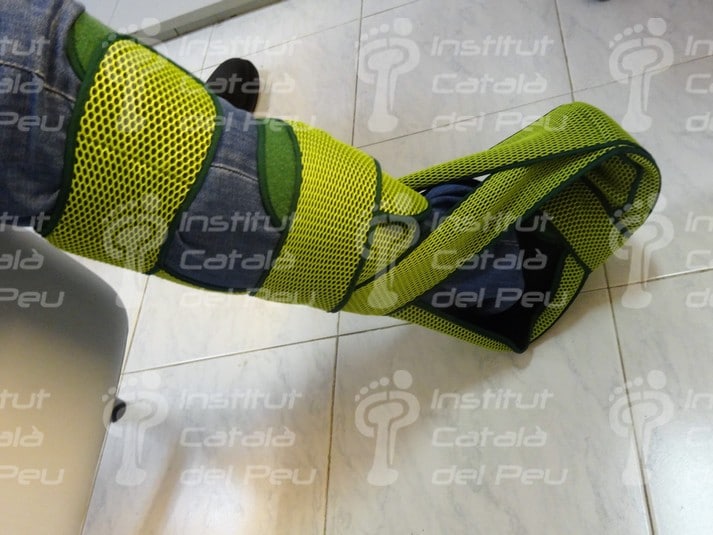

Domiciliated splint in order to stretch the fascia. Watch the dorsiflexion of toes.








Wonderful article, thanks for putting this together! This is obviously one great post.
A fantastic read.